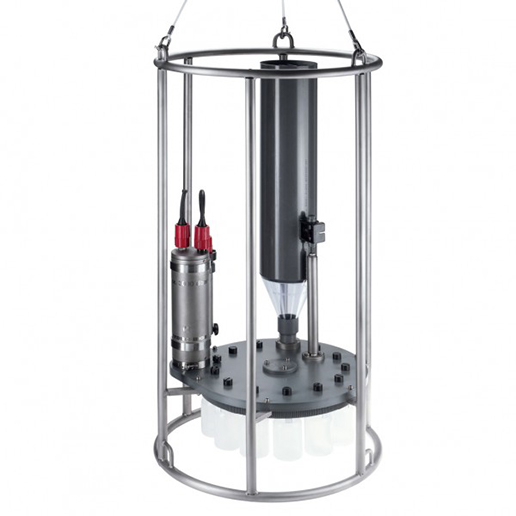
德国HYDRO-BIOS公司——多通道沉积物捕获器
Multi Sediment Trap
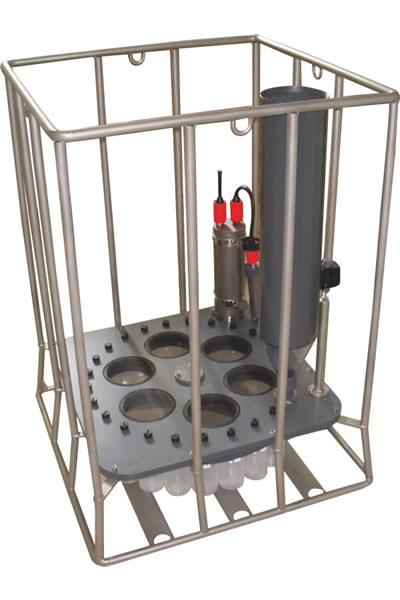



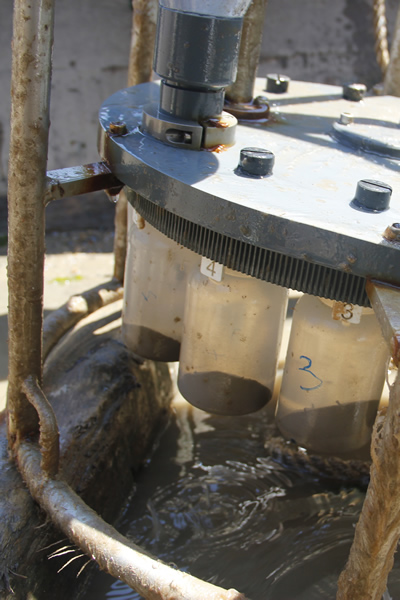
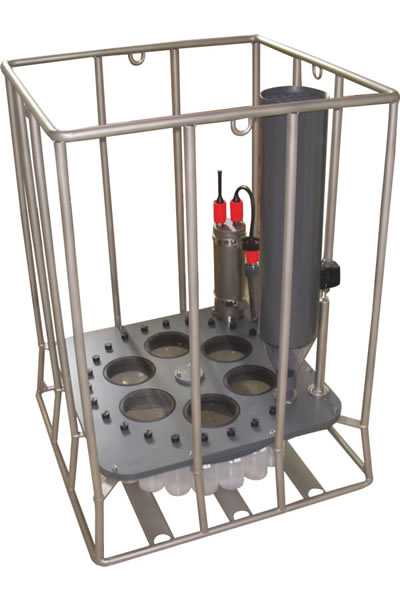
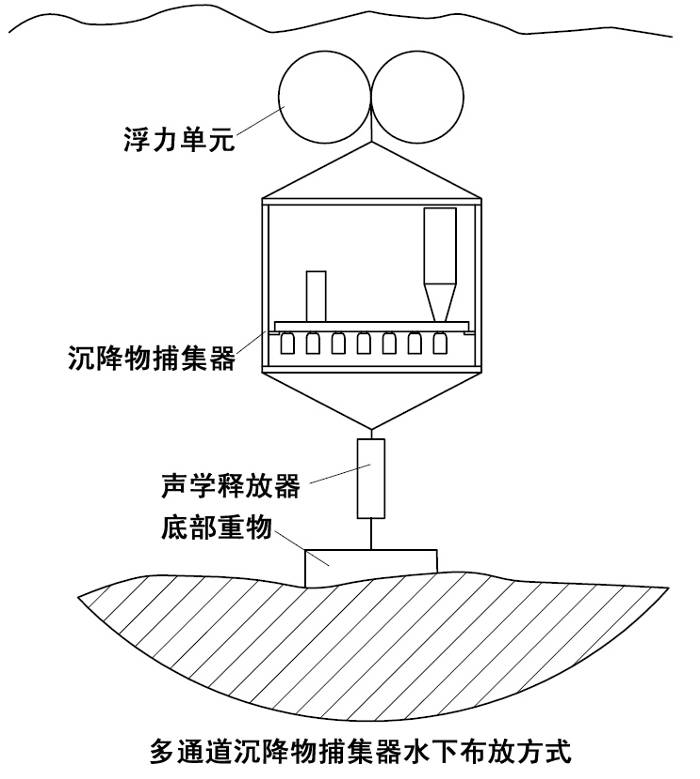
多通道沉降物捕集器的设计主要用于对相对垂直颗粒流较大的湖泊、大陆架和水栖∮环境的沉积物的自动采集。在北极、南极、热带、亚热带等环境中,经◥过无数次的长期野外操作,已经证明了它的可靠性。这╳款仪器不需要很重的固定线缆,它在较小的船上也可以很容易地安置和收回。多通道沉降物捕集器的控制装置可以执行为期一年多的时∏间依赖性工作。为了防止捕集到的沉降物从收集筒的上部被冲走,每个收集器在↘开口处都安装一个可拆卸∑的塑料网格,捕集器内部完全不含金属。当多通道沉降物捕集器的采集瓶←不工作时,它们与周围环境是隔离的。在布放和回收操作期↑间,收集筒底部是开放的,允许水流自动流过∞收集筒腔体。
整个系统由3节长时间锂电池供电。根据◥不同的需求,不同多通道沉降物捕集器的收集瓶数量可以★是6、12、24:豪华型多通道沉降物捕集器通过PC机上的一√个HYDRO-BIOS软件进行预编程,允许用★户实时(年、月、日、时、分)对每ξ个收集瓶的采样间隔单独预先设定,从1分钟至8760小时。豪华型采样器可通过增加各种参数的ζ 不同传感器进行升级,数据存储器容量可达4M。
豪华型多通道沉降物捕集器规格:
框架材质:钛合金
采样间◥隔设定:通过带OceanLab软件的电脑编程
开口面积:0.015平方米
沉降筒长:560mm
圆◣锥筒夹角:40度
沉降筒直「径与长度比例:1:4
最大操作深度:3000/6000/11000米
豪华型多通道沉降物捕集器订购指南:
货号 | 类型 | 尺寸 | 高度 | 空气中重量╲ | 水中重量 |
444 101 | 6瓶 | 直径320mm | 1200mm | 12kg | 5kg |
444 121 | 12瓶 | 直径520mm | 1040mm | 25kg | 10kg |
444 141 | 24瓶 | 800×800mm | 1000mm | 45kg | 20kg |
444 150 备用收集瓶,容积250ml,24个/套
444 160 备用锂电池→,3节/套

马达单元 数据处理软件
德国HYDRO-BIOS公司多通道沉降物捕』集器国内应用案例
1、水产养殖领域研究:
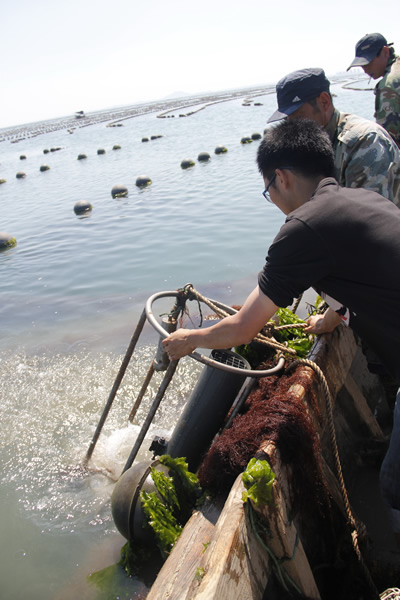
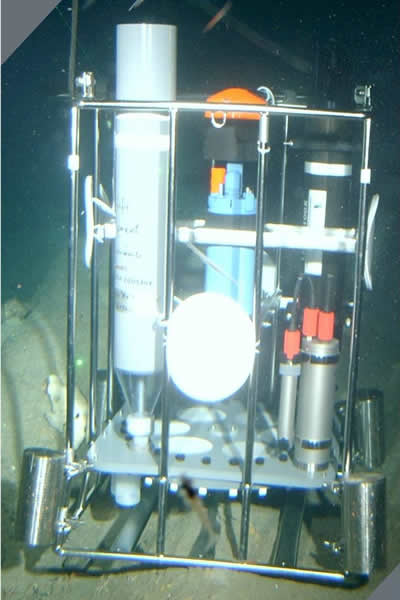
回收MST12 |
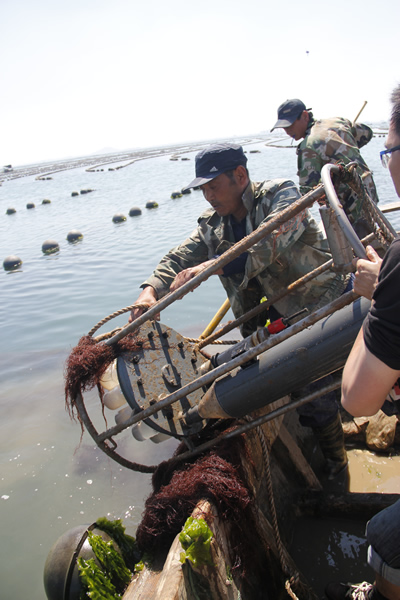
回收MST12 |
MST12捕集到的沉降物样品 |
MST12多通道沉降物捕集器和Multi Limnos自动水样采集器共同参与了山东某大型水产养殖企业海参养殖Ψ 区水体和沉降物之间营养物质循环的研究,获得了极其珍贵的数据,为今后饵料的投放建立了非常科学的数学〓模型,大大降低了企业的养殖成本。
2、海湾╱沉积动力学研究:
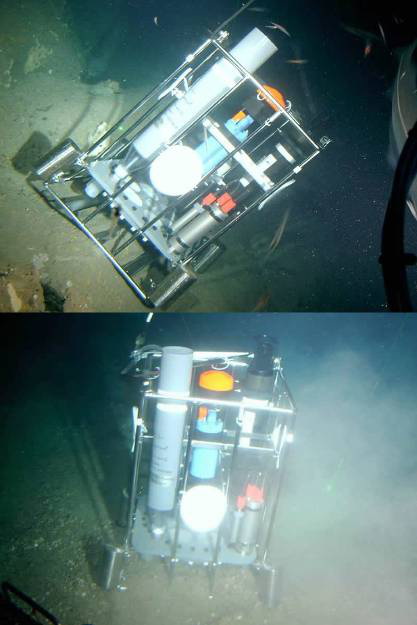
MST24 |
MST24坐底式布放 |
MST24坐底式布放 |
德国HYDRO-BIOS公司MST24多通道沉降物捕集器参与了国家海洋局罗源湾沉积动力学科研项目。罗源湾位于福建省沿海东北部,闽江口以北约50公里,是全∏国少有的天然深水港湾,可全天候靠泊30万吨轮船。罗源湾具备ㄨ建造东方大港的条件,从“十一五”期间开始,罗源湾成为福建省重点建设的港口。罗源湾在行政区划上隶属福州市,北岸属罗〓源县,南岸属连江县。根据海峡西岸经济区规划,列为福州港的深水外港。罗源湾在福建省◇、乃至中国港口的发展中有着非︼常重要的地位,对它的研究也势在必⌒行。科研人∩员将MST24长期坐底式布放在罗□源湾,成功捕集到了大量极具代表性的自然沉降物,为罗源湾沉积动力学的研究〇提供了真实可靠的数据。
代表文献:
1.Jürgen Lenz, Alvaro Morales, Judith Gunkel,1993.Mesozooplankton standing stock during the North Atlantic spring bloom study in 1989 and its potential grazing pressure on phytoplankton: a comparison between low, medium and high latitudes.Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography.40(1-2):559–572.
2.Dethleff, Dirk, Nürnberg, Dirk, Reimnitz, Erk, Saarso, Maart and Savchenko, Y.P.,1993.East Siberian Arctic Region Expedition '92: The Laptev Sea - its significance for Arctic sea-ice formation and transpolar sediment flux.Reports on Polar Research.120:3-48.
3.Bloesch Jürg,1996.Towards a new generation of sediment traps and a better measurement/understanding of settling particle flux in lakes and oceans: A hydrodynamical protocol.Aquatic Sciences.58(4):283-296.
4.A. Accornero, A. Bergamasco, A. Monaco, S. Tucci,1999.Particle Fluxes at the Edge of the Ross Ice Shelf: the Role of Physical Forcing.Oceanography of the Ross Sea Antarctica.177-195.
5.David N. Thomas, Hilary Kennedy, Gerhard Kattner, Dieter Gerdes, G. S. Dieckmann, Carl Gough,2002.Biogeochemistry of platelet ice: its influence on particle flux under fast ice in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica.Ecological Studies in the Antarctic Sea Ice Zone.169-179.
6.A. ACCORNERO, C. MANNO, K.R. ARRIGO, A. MARTINI and S. TUCCI,2003.The vertical flux of particulate matter in the polynya of Terra Nova Bay. Part I. Chemical constituents.Antarctic Science.15 (1): 119–132.
7.Alessandra Accornero, Marcia M. Gowing,2003.ANNUAL SEDIMENTATION PATTERN OF ZOOPLANKTON FECAL PELLETSIN THE SOUTHERN ROSS SEA: WHAT FOOD WEBS AND PROCESSESDOES THE RECORD IMPLY?.BIOGEOCHEMISTRY OF THE ROSS SEA ANTARCTIC RESEARCH SERIES.78:261-278.
8.P. Moreira-Turcq, J.M. Jouanneau, B. Turcq, P. Seylerd, O. Weber, J.L. Guyot,2004.Carbon sedimentation at Lago Grande de Curuai, a floodplain lake in the low Amazon region: insights into sedimentation rates.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology.214(1–2):27–40.
9.V. Ramaswamy, M.M. Sarin, R. Rengarajan,2005.Enhanced export of carbon by salps during the northeast monsoon period in the northern Arabian Sea.Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography.52(14-15):1922–1929.
10.J. C. Colombo, N. Cappelletti, J. Lasci, M. C. Migoya, E. Speranza, and C. N. Skorupka,2006.Sources, Vertical Fluxes, and Equivalent Toxicity of Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Coastal Sediments of the Río de la Plata Estuary, Argentina.Environmental Science & Technology.40(3), 734–740.
11.L. Roselli, C. Manno & G. Spezie ,2007.Inertial oscillations and particle flux interactions in a marine protected area in Gulf of Naples.Chemistry and Ecology.23(2):177-190.
12.C. Manno , S. Sandrini, L. Tositti, A. Accornero ,2007.First stages of degradation of Limacina helicina shells observed above the aragonite chemical lysocline in Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica).Journal of Marine Systems.68(1-2):91–102.
13.Jan Michels, Gerhard S. Dieckmann, David N. Thomas, Sigrid B. Schnack-Schiel, Andreas Krell, Philipp Assmy, Hilary Kennedy, Stathis Papadimitriou, Boris Cisewski,2008.Short-term biogenic particle flux under late spring sea ice in the western Weddell Sea.Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography.55(8-9):1024–1039.
14.C. Manno1, V. Tirelli, A. Accornero and S. Fonda Umani,2009.Importance of the contribution of Limacina helicina faecal pellets to the carbon pump in Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica).Journal of Plankton Research.32(2):145-152.
15.Andreas Kleeberg, Christiane Herzog, Michael Hupfer,2013.Redox sensitivity of iron in phosphorus binding does not impede lake restoration.Water Research.47(3):1491–1502.












